
Measurements at the Mauna Loa Observatory stopped after the 2022 eruption of the Mauna Loa volcano, when lava flow crossed the access road and took out power lines to the facility. The observatory remains inaccessible by vehicle and without power from the local utility company.
Observatory staff has established limited solar power in four observatory buildings and restored approximately 33 percent of the measurements onsite, including the Global Monitoring Laboratory and Scripps critical CO2 records and other atmospheric measurements.
Media can contact: Theo Stein (303) 819-7409 (theo.stein@noaa.gov) or Karin Vergoth 303-632-6413 (karin.vergoth@noaa.gov)
 National Oceanic and
Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Earth System Research Laboratory (ESRL)
National Oceanic and
Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Earth System Research Laboratory (ESRL)
Total Downwelling solar and thermal infrared radiation (or irradiance) is measured in units of Watts per square meter. Aaerosol optical depth is also measured.
We primarily use commercial thermopile broadband radiometers to measure the irradiance and aerosol optical depth, a measure of the total dust and particle load of the atmosphere, is measured with a sunphotometer.
| Measurement | Instruments | Frequency | Site |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Irradiance | Eppley Pyranometers with Q, OG1, and RG8 filters | continuous | MLO |
| Direct Irradiance | Eppley pyrheliometer with Q filter(2) | continuous | MLO |
| Direct Irradiance | Eppley pyrheliometer with Q, OG1, RG2, and RG8 filters | 3/day (weekdays) |
MLO |
| Direct Irradiance | Eppley/Kendall active cavity radiometer | continuous | MLO |
| Diffuse Irradiance | Eppley pyrgeometer with shading disk and Q filter (2) | continuous | MLO |
| UV Solar Radiation | Yankee Environmental UVB pyranometer (230-320 nm) | continuous | MLO |
| Diffuse (IR) Irradiance | Terrestrial downwelling IR pyrgeometer with shading disk | continuous | MLO |
| Column Water Vapor | 2 two-wavelength tracking sunphotometers: 860, 940 nm | continuous | MLO |
Solar and infrared radiation are fundamental ingredients in maintaining the current climate, and also play a major role in anticipated changes in that climate. Aerosol optical depth helps quantify the role of aerosol in radiatively forced climate change.
Read a MLO Solar Irradiance publication (.pdf format)
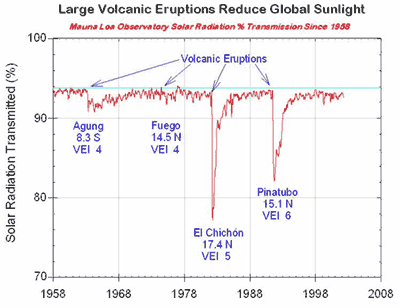
While no persistent long-term trends have been detected, there are excursions of several years in duration following major volcanic eruptions and there appears to be increased springtime aerosol loading in the last few years.
As the plot below shows, aerosols from large volcanic eruptions block some sunlight from reaching the earth's surface. Note how the lidar measurements of the volcanic aerosols in the stratosphere anti-correlate with the solar record.
Solar and thermal infrared (IR) radiation are vehicles for climate change but at the same time are affected by that change. Our radiation measurements can be used to investigate both the causes of and the response to climate change.
Dr. Ellsworth
Dutton
303-497-6660
Jim Wendell
303-497-6994
Paul Fukumura
808-933-6965 (x223)
1956